Abstract
Introduction
The international prognostic scoring system (IPSS) and its revised version (R-IPSS) are the most widely used clinical models for MDS risk stratification. Both models account for cytogenetic abnormalities captured by G-banding metaphase karyotyping. Among MDS patients, 50-60% will have a normal karyotype. MDS FISH panels are commonly applied to supplement cytogenetics. In small subsets of patients with normal karyotype, MDS FISH may detect cytogenetic abnormalities not resolved by metaphase karyotype. The utility of MDS FISH panel in refining IPSS or R-IPSS cytogenetic risk score among those patients is not known. We explored the impact of FISH in upstaging MDS patients with a normal karyotype and its prognostic value if incorporated into IPSS or R-IPSS cytogenetic risk score.
Methods
We identified patients with normal karyotype by G-banding who had cytogenetic abnormalities detected by an MDS FISH panel. The MDS FISH panel included probes for deletion (del(5)), del(7), del (20), trisomy 8 and del 17p. IPSS and R-IPSS was calculated based on karyotype as the standard recommendation and then recalculated according to cytogenetic abnormalities detected by the MDS FISH panel (FISH_IPSS and FISH_R-IPSS). Median overall survival (OS) was calculated from time of diagnosis using Kaplan-Meier estimates.
Results
Among 1600 patients in our MDS database with normal karyotype by G-banding, 53 patients (3%) had a cytogenetic abnormality detected by FISH. The cytogenetic abnormalities detected included del(7)/monosomy 7 in 25/53 patients (47%), del(5q)/monosomy 5 in 22/53 patients (42%), trisomy 8 in 14/53 (26%), del(20q) in 10/52 (19%), and 17p deletion in 1/10 (10%).
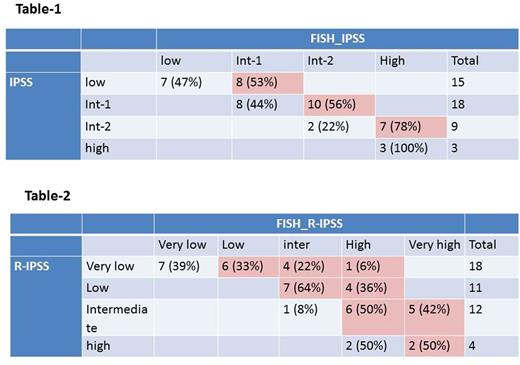
According to IPSS, 15 patients (33%) were classified as low risk, 18 patients (40%) as intermediate-1 (int-1), 9 patients (20%) int-2, and 3 patients (7%) as high risk. Table-1 summarizes restaging using FISH_IPSS where 53% of low risk IPSS were upstaged to int-1, 56% of int-1 upstaged to int-2, and 78% of int-2 upstaged to high risk.
By conventional R-IPSS, 18 patients (40%) were very low risk, 11 patients (24%) low risk, 12 patients (26%) intermediate risk, and 4 patients (9%) high risk. Upon restaging using FISH_R-IPSS (Table 2), 61% of very low risk patients, all low risk patients, 92% of intermediate risk patients, and 50% of high risk patients with FISH abnormalities were upstaged.
Among patients with low risk IPSS, median OS was 64 months (mo) for those low risk by FISH_IPSS and 61 mo for those upstaged to int-1 by FISH_IPSS. For patients with int-1 risk IPSS, median OS was 26 month for those int-1 by FISH_IPSS and 24.8 mo for those upstaged to int-2 risk by FISH_IPSS. Finally, for patients with int-2 risk IPSS, median OS was 30 mo for those classified as int-2 and 22 mo for those upstaged by FISH_IPSS.
Based on R-IPSS the median OS was 64, 24, 25 and 19 mo for very low, low, int, and high risk groups. Using FISH_RIPSS the median OS was 64, 61,30,21,22 mo respectively for very low, low, int, high and very high risk groups (p.003). Based on R-IPSS cytogenetic risk category all those patient were classified as good risk given normal karyotype with median OS of 30 mo. Based on FISH data if cytogenetic score was re-calculated accordingly, 16 patients remained good risk, 22 patients intermediate risk, and 14 patients high risk. The median OS was 30, 30 and 22 mo respectively.
Conclusions
FISH detected cytogenetic abnormalities in a small number of patients with normal karyotype by G-banding, which altered risk score assignment by IPSS and R-IPSS in a significant subset of positive patients.
Komrokji: Celgene: Honoraria; Novartis: Honoraria, Speakers Bureau. Sallman: Celgene: Research Funding. Padron: Incyte: Honoraria, Research Funding. Sweet: Ariad: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Karyopharm: Consultancy, Research Funding; Otsuka: Consultancy; Incyte: Research Funding; Pfizer: Consultancy; Novartis Pharmaceuticals: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau. Lancet: Pfizer: Other: Institutional research funding, Research Funding; Boehringer Ingelheim: Consultancy; Novartis: Consultancy; Celgene: Consultancy; Erytech: Consultancy; BioSight: Consultancy; Bio-Path Holdings: Consultancy; Janssen: Consultancy; Jazz Pharmaceuticals: Consultancy.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal